Season 10 Case 4
History: Abdominal Pain NOS
More Images?
Click Here for More Images
Answer:
CLICK HERE FOR ANSWER
Answer: Cardiac Myxoma (vs Lipoma)
A bit of an "incidentaloma", so not necessarily related to the patient's presenting symptoms, but a reminder not to cone down your view too much (as we used to say "Always look at the edges and corners of the film")
Findings:
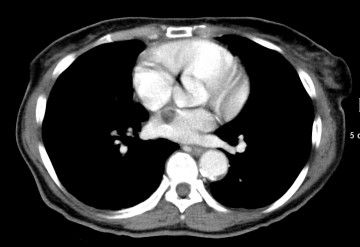
So we see a round low density mass that appears adherent to the intraatrial septum which forms a portion of the anterior wall of the left atrium. Notice the motion artifact around it consistent with it's motion during the cardiac cycle.
Cardiac Myxoma
-
Most common primary cardiac tumor in adults (kids think rhabdomyoma)
-
Benign
-
Can be any age
-
Female > male
-
Can be asymptomatic (found incidentally as this case was)
-
Can yield: arrhythmias (up to 20%), thrombus/emboli, valvular obstruction
Radiology
- typically a pedunculated mass with round shape
- Often mobile
- ~75% located in the left atrium (typically attached to the intraartial semptum - as we see here)
- If large, look for prolapse/abutment of the mitral valve
- CT: low density (can have internal Ca++ due to hemorrhage)
- MR: heterogeneous intermediate T1/T2 signal. Look for GRE blooming from calcium deposits (old hemorrhage?), + enhancement
- Look for evidence of evidence of vascular obstruction (dilated atrium)
Differential Diagnosis:
- Intracardiac thrombus
- Classically these are located in the left atrial appendage or left ventricular apex (post LV infarct)
- But myxoma and thrombus can look similar. Both can be mobile
- Key differentiation is +Enhancement on MRI for myxoma (obvious ot thrombus right!)
- Other primary cardiac tumors
- Cardiac lipoma - This is another possibility for our case here (hard to tell without density measurement and with the artifact). They can look very similar but uniformly low density (fat). MRI intensity will follow that of fat
- Rhabdomyoma (most common in kids)
- papillary fibroelastoma (typically smaller mass associated with aortic or mitral valve)
- Angiosarcoma (most common malignant tumor - usually right atrium and extend through the myocardium into the pericardium - "uglier" than myxoma)
Treatment
Typically prompt surgical resection is curative without further increased risk of mortality